how do glasses work physics
How the eye works is that natural lenses are able to bend the light that passes through it into a clear right-side-up image. Anti-Fog coating will minimise the accumulation of fog on the lens of spectacle.

Pin By Alex Mazika On Colloids In 2021 Physics Real Glass
Refraction is the term given to how light slows and bends when it passes from a light-density medium such as air into the thicker density of transparent glass or plastic.
. Prescription eyewear otherwise known as eyeglasses prescription sunglasses or contact lenses works by bending light as it enters your eye to allow it to focus perfectly on your retina for a crystal clear viewing field. A few different parts of the eye make this possible. So basically our brain takes two 2D images from our eyes and interprets them as 3D.
Convex lenses correct nearsightedness by refracting the light toward the bottom and the top of the lens so. In these there are two types Linearly Polarized Glasses. For glasses that correct for near sighted people this also means a reduction in size of the image on the retina.
30 x 10 8 ms. 3D glasses try to replicate this. For contacts which are much closer to the lens the size distortion is much less.
As the strength of the lens increases the focal point becomes longer. There are some more complicated systems as well but because they are expensive they are not as widely used. Glasses are cut to change the focal length of the light entering the eye so it hits the focal point properly and the wearer can see without blurring.
Glasses are cut to change the focal length of the light entering the eye so it hits the focal point properly and the wearer can see without blurring. The eyeglass lens is simply used to create an image of the object at a distance where the nearsighted person can see it clearly. When a beam of light passes through any curved piece of glass it has a tendency to either expand the beam and spread it out or make the beam narrower eventually into nothing then expand again.
S M and L and they are responsible for identifying the colors blue green and red respectively. You will be amazed at how complex and sophisticated a simple pair of dark glasses can be. Whereas someone not wearing glasses can see clearly objects that fall between their near point and their far point someone wearing glasses can see images that fall between their near point and their far point.
These glasses are used when two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen through orthogonal polarizing filters Usually at 45 and 135 degrees. The lenses control what each eye sees by filtering the light going to each eye only letting certain wavelengths pass. Light hits the glass at an angle and it.
In 3D glasses one lens is one colour and the other is another colour. The lens of the eye will need to compensate for closer objects. In fact if the image of the lens is at infinity you wont even have eye stra.
This is how normal eyes work. The blue cones usually operate disjointly whereas for most people the red and. To better understand this process we first need to understand how the eye itself functions.
Essentially electromagnetic waves are transversely oscillating electric and magnetic fields that travel at the speed of light. We can observe the dynamics of refraction most clearly by dipping a pencil into water and observing how it no longer appears straight. With the glasses back on your brain merges those images to create the perception of depth.
The glasses allow only one of the images into each eye because they contain lenses with different polarization. There is nothing more sensitive than eyes. So making glasses is all about changing the focal length and point of focus so.
Glasses with Polarizing Filters. How Do Glasses Work. Then all the human physiology and brain processing power goes to work to analyze the differences between the images and create the effect of a three-dimensional image.
Individuals with myopia nearsightedness use eyeglasses to see far away. This in turn becomes a measure of how far away an object is. A magnifying glass is usually a convex lens a lens that bulges outwards made of either glass or plastic.
Its all about getting things closer to your eye while still keeping focused. There are three types of cones. A minus lens is thickest at the base thus the light is spread away from the lens center.
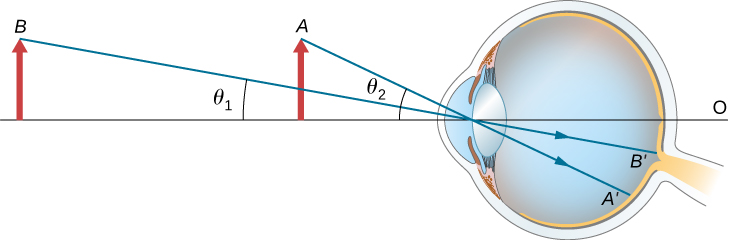
Light hits the glass at an angle and it. The viewer wearing linearly polarized glasses can see only one image in each eye the one which has same polarizing angle. To put it very simply the eye gathers information and focuses the light through a lens to make an image - just like a camera.
And the UV coating will restrict the passage of UV rays towards the eye-sight. Our eyes detect colors using cones. Well analyze the different styles and look at the technology behind the different lens compositions.
Electromagnetic radiation refers to waves that propagate through electromagnetic fields. A minus lens is used to correct myopia by pushing the focus farther back. Lastly the crossed polarizing filters on the two lenses of the dorky glasses ensure that each eye sees only one of the images the one for that eye.
The polarized glasses allow only one of the images into each eye because each lens has a different polarization. This is how a scene might look if you took off your glasses during a 3D movie. Electromagnetic radiation is characterized into a continuous spectrum based on frequencywavelength see Figure 2.
Nearsighted corretion places virtual images of far objects on the retina. The Scratch Resistant coating will reduce the chances of scratch on the spectacles. Different Lenses For Different Problems Through the pupil light enters the eyes and gets focused by the lens into the retina.
Brand Physics Behind Glasses. You will also learn how light works and see why light in certain situations can make sunglasses absolutely essential. If that is the case here are some of the things you need to know about how glasses work.
Glasses are comprised of lenses that bend light.

Physics Optics Light Refraction Snell S Law Prism Physics Refraction Optical

Prism Lenses For Your Eye Glasses Eye Facts Computer Vision Syndrome Lenses

How To Get The Thinnest Lenses For Your Prescription Zenni Optical Eyeball Diagram Eye Sight Improvement Lenses

Diagram On How Polarized Lenses Work

Types Of Spherical Lenses 1 Basic Physics Lens Physics Notes
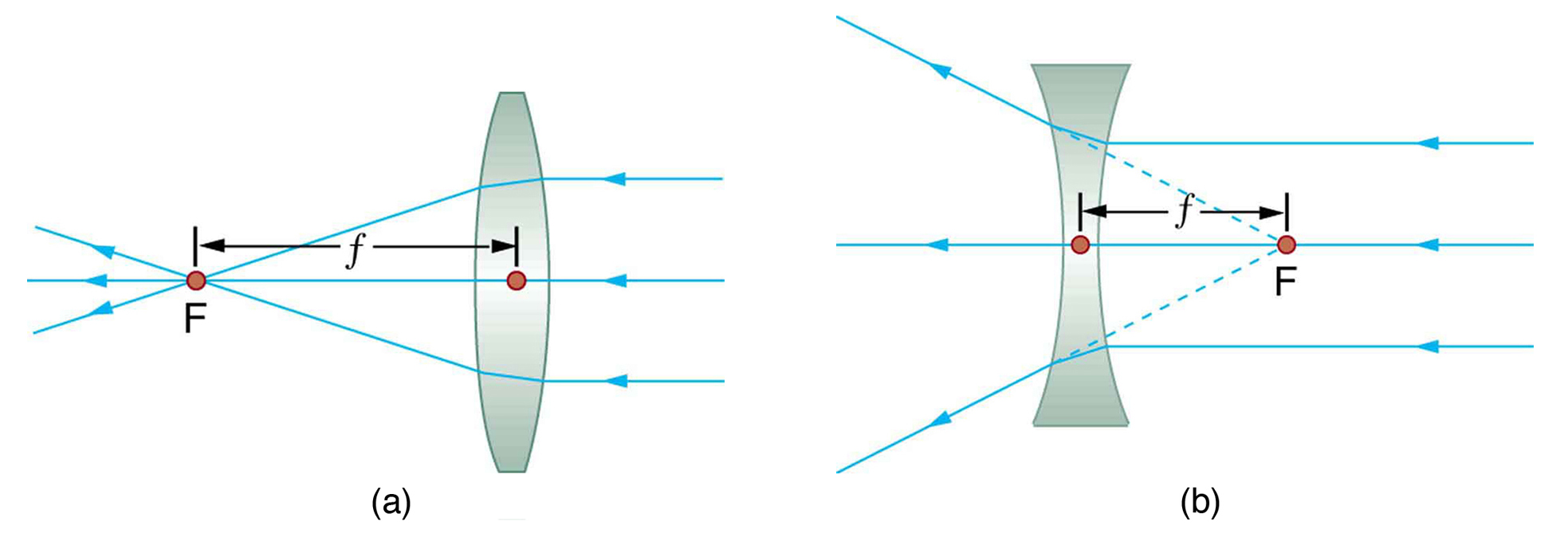
Image Formation By Lenses Physics

Lesson 6 Emmetropia Myopia Lesson Learning Optical

Physics Optics Lenses Diverging Lens 2 Physics Optical Lens

Rbse Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Alternating Current Rbsesolutions Rbsesolutionsforclass12physicschapter10 Alternating Physics Class Solutions
The Simple Magnifier University Physics Volume 3

Lesson 3 Lens Power Power Lens Lesson
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

Physics Optics Lenses 1 Of 4 Converging Lens Youtube


